
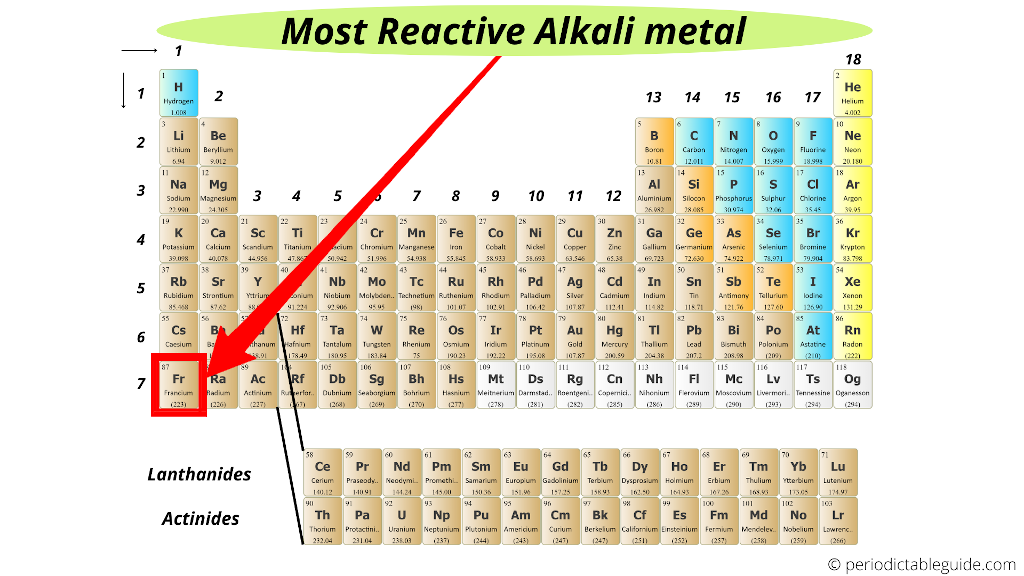
All the alkali metals react with water, with the heavier alkali metals reacting. This trend occurs because each element, as you move down. They react with water to produce an alkaline metal hydroxide solution and. Hence the largest molecules can not exceed that(slightly larger than the reacting water molecules one layer deep).The reaction been equated to a capacitor going off with electron coming from the surface alkaline ions to water. Caesium, the fifth alkali metal, is the most reactive of all the metals. The Alkali Metals become more reactive moving down in the group, with francium being the most reactive. Edexcel Group 1 - the alkali metals The group 1 elements are all soft, reactive metals with low melting points. The alkali metals are very reactive, readily losing 1 electron to form an ion with a 1+ charge: M M + + e Due to this reactivity, the alkali metals are found in nature only as compounds. The surface tension of the Na/K drop can be estimated to be coulombically unstable for radius greater than 5 angstroms. In a reaction, this electron is lost and the alkali metal forms a +1 ion. The breakdown is know as Coulomb fission and is defined as the ratio between the droplet Coulomb self-energy and twice its surface energy. All alkali metals have one electron in the outer shell. The atomic radius(alkaline ions') may take part through the ratio to waters molecules radius. High ionization then exceeds the stability of the molecules themselves which is the Rayleigh instability limit. alkali metal, any of the six chemical elements that make up Group 1 (Ia) of the periodic table namely, lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). This was a observed with use of high speed cameras to follow the process with a 100 μs time resolution.
A sodium/potassium ,alloy which is liquid at room temperature, is good example of a alika reaction and shows the effects in question clearly and in useful for testing this idea.Įxperiments have been done to confirm this under argon atmosphere and when delivered by a syringe with a well-defined amount of the metal alloy(Na/K) it gives an consistent unoxidized surface,leading to controlled explosions and taking out possibility of side reactions being the initiator of such high rate of reaction.
The general electronic configuration of these elements is ns2. Likely, it's caused by ionization that act on water molecules through coulombic reaction. They are also highly lustrous (shiny) and are quite reactive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
